How to Set Up DKIM for SpamTitan?

DKIM works by adding a digital signature to outgoing email messages. This signature can be verified by the receiving email server, which can then determine whether or not the message has been tampered with during transit. In order for DKIM to work, the sending email server must generate a cryptographic key pair, which consists of a private key and a public key. The private key is used to sign outgoing email messages, while the public key is published in the Domain Name System (DNS). When an email message is signed with DKIM, the signature is added as a header to the message. The receiving email server can then use the public key to verify the signature and confirm that the message has not been altered.
Steps to Configure DKIM for SpamTitan
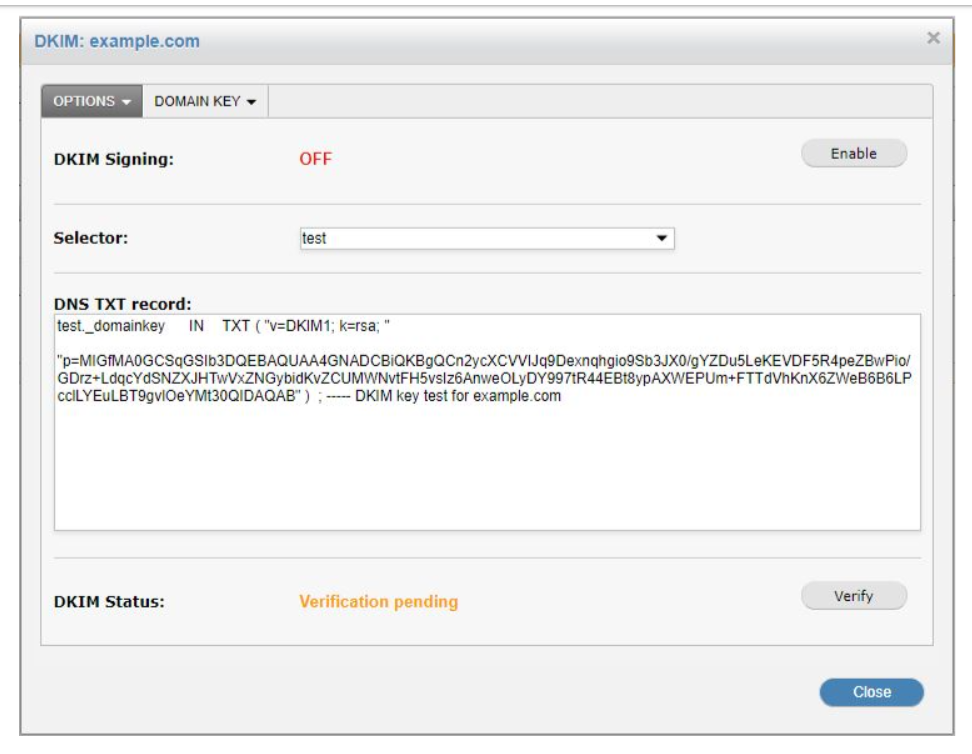
- Go to Mail Relay > System Setup > DKIM. Your list of domains is displayed.
- Select the edit button next to a domain. An additional window will open.
- Navigate to the DOMAINKEY tab.
- Enter a selector name in the selector field.
- Select create, then click the option tab.
- Make a copy of the DNS TXT record and add it to your DNS.
How to Get Your DKIM Public Key Available for SpamTitan
- Sign in as the administrator to your DNS provider’s administration console.
- Go to the DNS records section of each of your domains.
- Depending on the type of DKIM record that has been provided to you, generate a TXT or CNAME record.
- Copy and paste the hostname and value
- Save your record’s modifications and wait 48–72 hours for your DNS to take effect.
You can use Skysnag’s free DKIM Checker to check the health of your DKIM record here
Enable DMARC for your domains to protect against spoofing. Sign up for a free trial today!
For more information on SpamTitan DKIM setup, you can refer to their reference documentation






